Home
People
Projects
Research
topics
Publications
Contact |
Planned projects
| Cognitively Inspired Pattern Discovery methods for latent and Associative model
Learning (CIPDAL) |
The aim of CIPDAL is to
i) develop new, cognitively motivated pattern discovery methods, and
ii) to create new knowledge
and theory regarding computational learning, focusing especially on aspects of language acquisition.
Model learning can be seen as a method to organize and compress incoming patterned information.
Once learned, the model works as an active memory storing the necessary structures for new and emerging cognitive skills.
See also Hybrid Model Learner (HML)
|
Current projects
| Acquisition of Communication and Recognition Skills (ACORNS) |
The ACORNS project intends to develop, implement and test mathematical models and computational
mechanisms needed to create an artificial agent that is capable of acquiring human verbal communication
behaviour based on recent findings related to emergence as well as the memory-prediction theory of intelligence.
Unlike conventional pattern recognizers, the ACORNS agent will learn dynamic emergent patterns of speech and
non-speech sounds from rich and redundant representations of the acoustic input. Learning will be guided by
the agent's intention to fulfill basic needs required to acquire the verbal and non-verbal communication skills,
similar to the acquisition of language and communication skills of a human toddler.
 |
| Parallel activations of word memory-traces from speech stream. |
The TKK Speech Technology Team (STT) is involved in several aspects of project, the main tasks being speech segmentation,
signal patterning, and unsupervised pattern discovery from the input. STT is also involved in building of multilingual corpora containing
both infant- and adult-directed speech that can be used to study cognitively plausible computational models of language acquisition.
ACORNS is funded by European Union Sixth Framework Programme (FP6), Future Emerging Technologies, contract no. FP6-034362.
|
| Automatic recognition of bird species by their sounds (Avesound) |
In Avesound project techniques and systems for automatic identification of sounds produced by birds (Aves) are developed.
The main emphasis of Avesound is to develop algorithms for the automatic recognition of bird species. The long term goal of
the research is to develop a system capable of recognizing a majority of Finnish bird species from a continuous environmental
recording.
The methods will be tested with species where data from multiple individuals is already available or will be
collected during the project. Due to specific properties of bird sounds, it is necessary to develop new signal processing
and pattern recognition techniques which are particularly suitable for the identification of bird sounds. The approach is
to take into account the physics of sound production in birds and structural and statistical characteristics of bird songs
and calls.
The developed methods have some important applications in biology. At a higher level, a generic framework for
identification of animal sounds will be developed in the project. This framework will be applicable also to the development
of identification techniques for other classes of animals such as mammals, amphibians, and insects.
Avesound is being funded by Academy of Finland.
|
Past/inactive projects
Many people around the world have reported that while a bright and actively moving aurora
is visible in the sky, strange sounds - not typically heard at the places of observation
- have been heard.
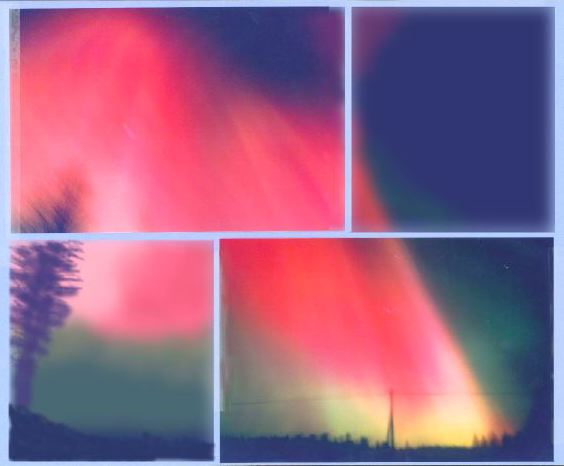 |
| Aurora borealis above southern Finland in 2000. |
To investigate these observations, the "Aurora" project was launched in the spring of
2000. The main goal of the project was to record and analyze aurora related sounds.
Evidence through careful measurements at ground level have indicated that at least some
of the strongest geomagnetic storms are able to produce perceivable sounds. What was also
discovered was that the fluctuations in sound pressure level correlate with the
fluctuations occurring in geomagnetic activity in a statistically significant manner.
This indicates the possibility that sound is created in some manner from geomagnetic
storms (Aurora Borealis) under favourable weather conditions.
|
| Towards a Listening Machine: Segmentation, classification, and interpretation of sounds |
| The objective of this project is to work towards a "Listening Machine" (LM) - a system that recognizes and
interprets sounds. Such a machine could be applied in many different fields such as speech recognition and speaker recognition
/verification, industrial sound analysis, audio surveillance systems, aids for the hearing-impaired, and the analysis of natural
soundscapes. |
| Speech-To-Text: Phonemic Speech Recognizer for Finnish |
Development and testing of state-of-the-art methods for recognition of Finnish phonemes, and development
of a novel prototype for automatic phoneme recognizer. The aims include robust, speaker independent, and unlimited vocabulary
recognizer prototype that is able to translate continuous speech to text.
|
|
